Barcode
A barcode is a machine-readable code that contains numbers and parallel lines of different widths representing product information, such as product code, type, and location.
Updated: October 12, 2023
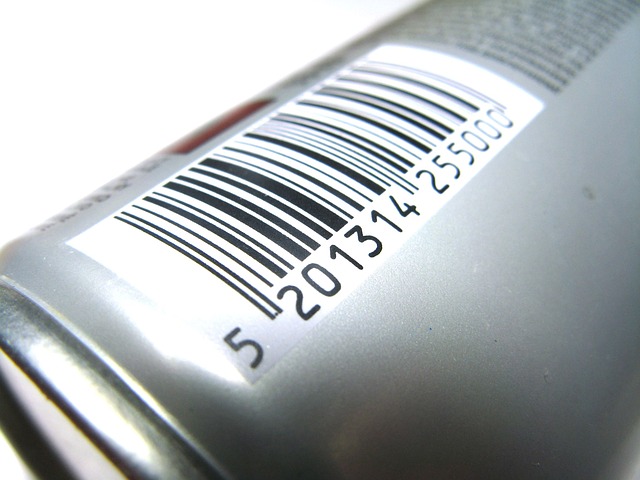

A barcode is a machine-readable code that contains numbers and parallel lines of different widths representing product information, such as product code, type, and location. They are used to help identify products. Varying templates are used by different countries and industries to print barcodes on products to meet their specific requirements.
Barcode software can be used to keep track of stock levels, product locations, and raw materials. It reduces potential human error by automating the data entry process.
Product information are used by manufacturers and other e-commerce businesses to make data-driven business decisions and improve productivity and efficiency. The basic information about the product can be easily read by the scanning device and automatically entered into a computer system or database with the lines and patterns on a barcode which reduces the time taken to record product information manually. Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags can also be generated or scanned by some barcode software for asset tracking.
Universal product codes (UPCs) are one of the most commonly used out of the multiple types of barcodes available. 1-dimensional barcode and 2-dimensional barcode are two main categories of barcode systems. 1-dimensional barcodes are a series of black and white bars that defines product type, color, and size information. UPC, European Article Number (EAN), Code 39, and Code 128 are some of the examples. 2-dimensional barcodes are more complex and can display product images, inventory levels, and prices.